Accelerating Industry 4.0 digitalization and innovation. Critical networks purpose-designed for your digital-era success
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, enables enterprises, governments and public sector agencies to use innovative digital technologies, smart automation and advanced analytics to transform their operating processes. This blending of technologies creates a convergence of the physical and digital worlds, enabling an era of massive industry improvements and positive impacts for societies.
The journey to Industry 4.0 is powered by ubiquitous connectivity, cloud computing and rich data. It requires high-performance networks that can integrate with legacy environments to support critical processes with strong security, 24/7 availability, high speed and ultra-fast responsiveness. These networks must connect all machines, people and processes and offer deep data insights that can enable agile and proactive operations.
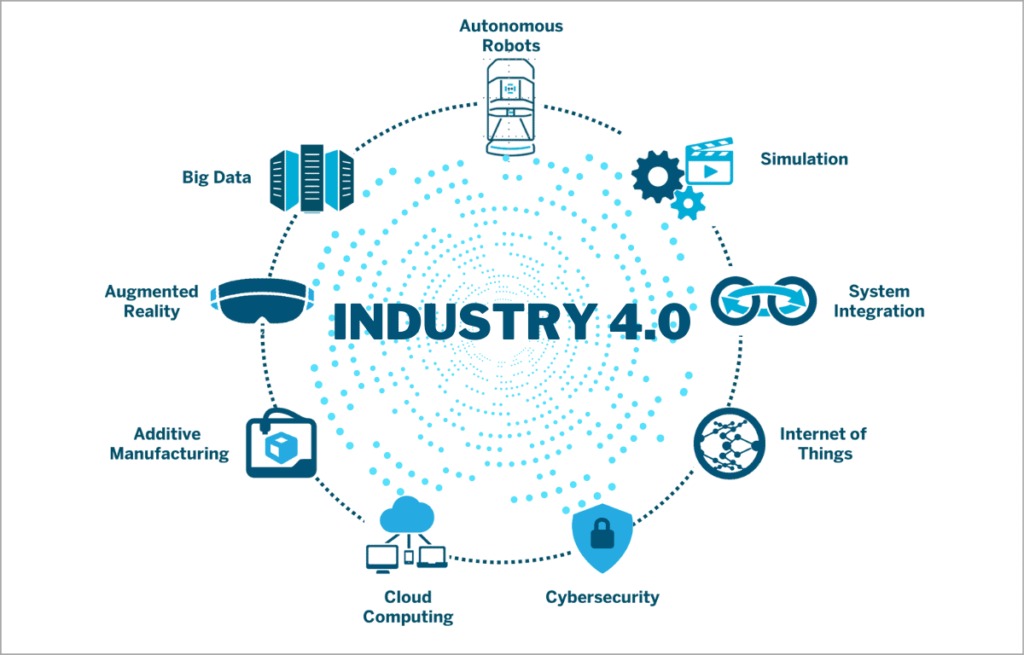
- Big Data and AI analytics: In an Industry 4.0 landscape, Big Data is collected from a wide range of sources. Of course, this includes capturing data from assets, equipment, and IoT-enabled devices. Data sources also extend outside the factory floor, into other areas of the business and the world. They can include everything from customer reviews and market trends that inform R&D and design, to weather and traffic apps that help ensure smoother logistics. Analytics powered by AI and machine learning are applied to the data in real time – and insights are leveraged to improve decision-making and automation in every area of manufacturing and supply chain management.
- Horizontal and vertical integration: An essential framework of Industry 4.0 is horizontal and vertical integration. With horizontal integration, processes are tightly integrated at the “field level” – on the production floor, across multiple production facilities, and across the entire supply chain. With vertical integration, all the layers of an organization are tied together – and data flows freely from the shop floor to the top floor and back down again. In other words, production is tightly integrated with business processes like R&D, quality assurance, sales and marketing, and other departments –reducing data and knowledge silos and streamlining operations.
- Cloud computing: Cloud computing is the “great enabler” of Industry 4.0 and digital transformation. Today’s cloud technology provides the foundation for most advanced technologies – from AI and machine learning to IoT integration – and gives businesses the means to innovate. The data that fuels Industry 4.0 technologies resides in the cloud, and the cyber-physical systems at the core of Industry 4.0 use the cloud to communicate and coordinate in real time.
- Augmented reality (AR): Augmented reality typically overlays digital content on to a real environment. With an AR system, employees use smart glasses or mobile devices to visualize real-time IoT data, digitalized parts, repair or assembly instructions, training content, and more – all while looking at a physical thing like a piece of equipment or a product. AR is still emerging but has major implications for maintenance, service, and quality assurance, as well as technician training and safety.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): The Internet of Things (IoT) – more specifically, the Industrial Internet of Things – is so central to Industry 4.0 that the two terms are often used interchangeably. Most physical things in Industry 4.0 – devices, robots, machinery, equipment, products – use sensors and RFID tags to provide real-time data about their condition, performance, or location. This technology lets companies run smoother supply chains, rapidly design and modify products, prevent equipment downtime, stay on top of consumer preferences, track products and inventory, and much more.
- Additive manufacturing/3D printing: Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing was initially used as a rapid prototyping tool but now offers a broader range of applications, from mass customization to distributed manufacturing. With 3D printing, parts and products can be stored as design files in virtual inventories and printed on demand at the point of need – reducing both costs and the need for off-site/off-shore manufacturing. Every year, the extent of 3D printing grows more varied, increasingly including base filaments such as metals, high-performance polymers, ceramics, and even biomaterials.
- Autonomous robots: With Industry 4.0, a new generation of autonomous robots is emerging. Programmed to perform tasks with minimal human intervention, autonomous robots vary greatly in size and function, from inventory scanning drones to autonomous mobile robots for pick and place operations. Equipped with cutting-edge software, AI, sensors, and machine vision, these robots are capable of performing difficult and delicate tasks – and can recognize, analyze, and act on information they receive from their surroundings.
- Simulation/digital twins: A digital twin is a virtual simulation of a real-world machine, product, process, or system based on IoT sensor data. This core component of Industry 4.0 allows businesses to better understand, analyze, and improve the performance and maintenance of industrial systems and products. An asset operator, for example, can use a digital twin to identify a specific malfunctioning part, predict potential issues, and improve uptime.
- Cybersecurity: With the increased connectivity and use of Big Data in Industry 4.0, effective cybersecurity is paramount. By implementing a Zero Trust architecture and technologies like machine learning and blockchain, companies can automate threat detection, prevention, and response – and minimize the risk of data breaches and production delays across their networks.